Table of Contents
In the world of carbon fiber, selecting the right material is crucial for any business aiming to achieve the perfect balance between performance, cost-efficiency, and product quality. Whether you’re in the automotive industry, aerospace, or sports equipment manufacturing, understanding the differences between wet carbon fiber and dry carbon fiber can help you make informed decisions that will improve your products and processes.

At JCSPORTLINE, we’re not only dedicated to providing high-performance carbon fiber solutions but also focused on helping businesses optimize production through cost-effective material selection. In this blog, we’ll dive deep into the differences between wet carbon and dry carbon, explore their respective advantages, and discuss how to choose the right material for your specific business needs.
Best Guide to Wet Carbon Fiber: Cost-Effective Solutions for Budget-Sensitive Projects
Wet carbon fiber, often referred to as hand-laid carbon fiber, is made by coating carbon fibers in liquid resin, followed by a vacuum-sealing and curing process. The name “wet” comes from the glossy appearance created by the resin coating. The production process for wet carbon is simpler and more cost-effective, which makes it a popular choice for projects that prioritize budget over extreme performance.
Key Characteristics of Wet Carbon Fiber:
- Manufacturing Process: The carbon fiber is coated with liquid resin and vacuum-sealed before being cured. This simpler process requires less expensive equipment and results in a glossy “wet” finish.
- Cost: Wet carbon is less expensive than dry carbon due to its less complex manufacturing process and the use of cheaper materials and equipment.
- Strength: Wet carbon has lower strength compared to dry carbon, as it is more prone to air bubbles and wavy fiber weaves, which can affect the overall performance and durability.
- Weight: Wet carbon is heavier than dry carbon because the resin is applied externally, adding extra weight to the material.
- Maintenance: Wet carbon requires proper maintenance to prevent yellowing, deformation, and loss of aesthetic appeal over time.

Top Reasons to Choose Dry Carbon Fiber: High-Performance Material for Demanding Applications
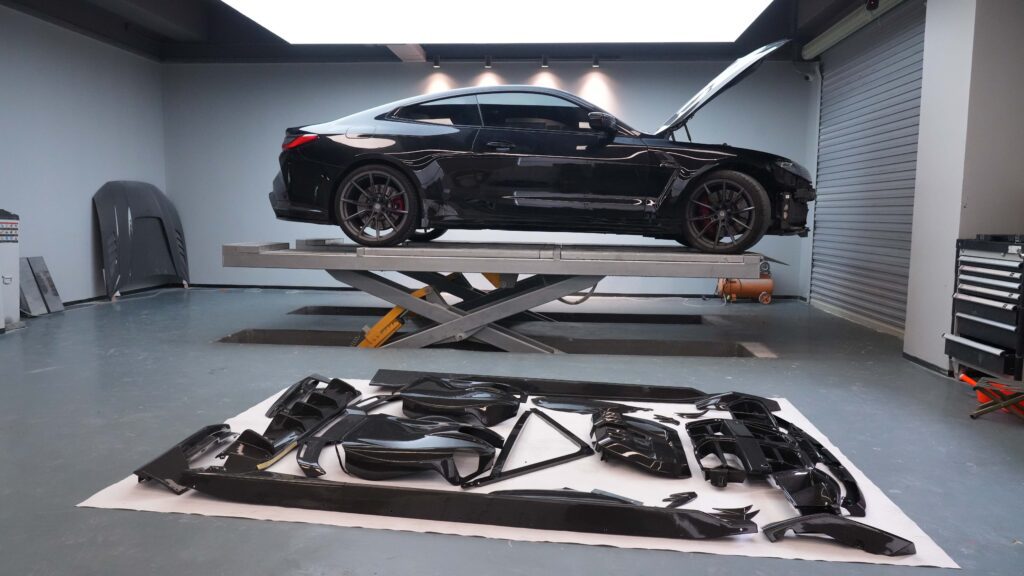

Dry carbon fiber, also known as prepreg carbon fiber, is manufactured by combining resin with carbon fibers before curing in a high-pressure autoclave. Unlike wet carbon, the resin is pre-impregnated into the fiber, which ensures higher strength and lighter weight. The high-performance nature of dry carbon makes it the material of choice for industries that demand extreme durability and precision.
Key Characteristics of Dry Carbon Fiber:
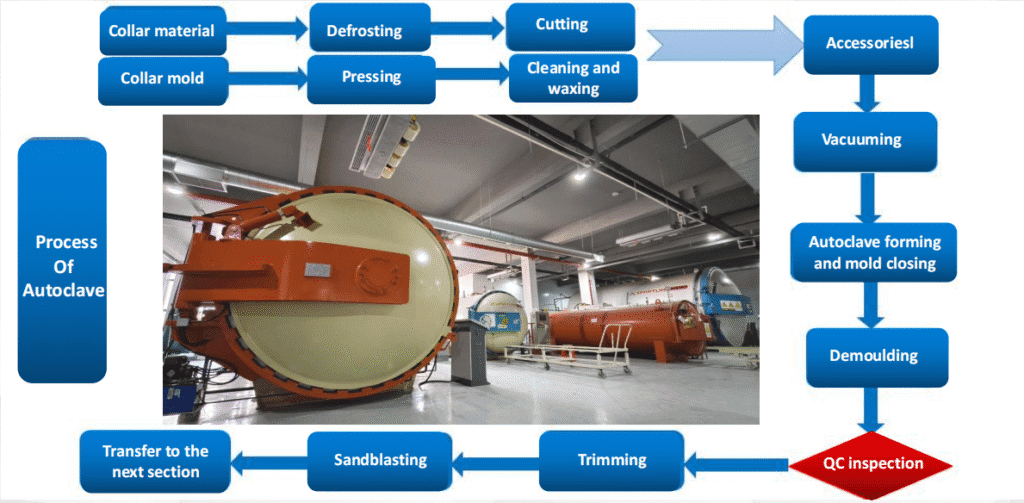
- Manufacturing Process: Pre-impregnated carbon fibers (prepreg) are placed in an autoclave for high-pressure curing, which removes impurities and strengthens the material significantly.
- Cost: Dry carbon is more expensive due to the prepreg process and the need for autoclave equipment, which require higher initial investment and operational costs.
- Strength: Dry carbon is stronger because the autoclave process eliminates air bubbles and other imperfections, providing superior mechanical properties.
- Weight: Dry carbon is lighter than wet carbon because the resin is baked into the fibers, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical.
- Maintenance: Although dry carbon requires maintenance to preserve its appearance and performance, it lasts longer and generally requires less frequent repairs due to its superior durability.
🔘 Get A Custom Quote
🔘 Contact Our Sales Team
How to Choose Between Wet Carbon Fiber and Dry Carbon Fiber: Complete Guide for Businesses
Deciding between wet carbon and dry carbon depends on your specific business needs. Whether you’re developing a cost-effective product or a high-performance component, understanding the trade-offs between the two materials will guide your decision-making process. Here’s a complete guide to help you select the right carbon fiber for your projects.
Wet Carbon vs Dry Carbon: How to Make the Best Choice:
- Performance Needs:
- If your project requires high strength and lightweight materials (such as in racing, aerospace, or high-end automotive parts), dry carbon is the optimal choice.
- If the project focuses more on cosmetic enhancement and budget is a key concern, wet carbon can be a cost-effective solution.
- Budget Considerations:
- Wet carbon is ideal for businesses looking to reduce production costs without compromising on aesthetic quality. It’s perfect for aftermarket parts, decorative pieces, and non-performance applications.
- If your business requires extreme performance and long-term durability, investing in dry carbon will provide better returns in terms of product longevity and customer satisfaction.
- Market Demand:
- For products that need to meet OEM standards or performance-critical applications, such as motorsports, aircraft, and sports equipment, dry carbon is necessary.
- If your market primarily involves mass production of non-structural parts, wet carbon is a suitable choice, providing a balance of affordability and adequate performance.
At JCSPORTLINE, we provide both wet carbon and dry carbon solutions that are tailored to your business needs. Our expertise helps you optimize your production process while ensuring high-quality results at a competitive price.

Top 5 FAQs About Wet Carbon and Dry Carbon Fiber: Common Questions Answered
1. Why is dry carbon more expensive than wet carbon?
Answer:
Dry carbon is more expensive than wet carbon because it requires prepreg carbon fiber and autoclave curing equipment, which are more costly. The prepreg process ensures higher strength and lighter weight by embedding resin directly into the fibers, whereas wet carbon is produced with a simpler method, using externally applied resin.
2. Can wet carbon be used for high-performance applications?
Answer:
While wet carbon can be used for some low-performance applications, it is not suitable for high-performance industries like motorsports or aerospace, where strength and weight reduction are critical. Dry carbon is the preferred material for these applications due to its superior mechanical properties and long-term durability.
3. How long does dry carbon last compared to wet carbon?
Answer:
Dry carbon lasts significantly longer than wet carbon because the autoclave curing process removes air bubbles and impurities, making it more durable and resistant to wear. Wet carbon, on the other hand, is prone to deformation and wear and tear over time, especially when exposed to extreme conditions.
4. What are the maintenance requirements for wet and dry carbon?
Answer:
Both wet carbon and dry carbon require proper maintenance to preserve their appearance and performance. Wet carbon needs regular cleaning and UV protection to avoid yellowing. Dry carbon requires less frequent maintenance, but it should still be cleaned with gentle products to prevent damage and preserve its finish.
5. Which industries benefit most from dry carbon fiber?
Answer:
Dry carbon is best suited for industries that demand extreme performance, such as motorsports, aerospace, and high-end automotive manufacturing. It is also ideal for sports equipment like bicycles and surfboards, where strength, light weight, and durability are essential.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Carbon Fiber for Your Business
Choosing between wet carbon and dry carbon ultimately depends on your project’s specific needs. At JCSPORTLINE, we offer both wet carbon and dry carbon solutions that meet various performance and budget requirements. Our advanced mold material solutions further optimize production costs while maintaining the highest standards of quality.
If you have any questions or want to explore the best carbon fiber solutions for your business, feel free to contact us today. Our engineering team will help you choose the right material and provide a cost-effective solution for your production needs.
For further reading on composite materials, including carbon fiber, check out the Wikipedia page on Composite Materials.